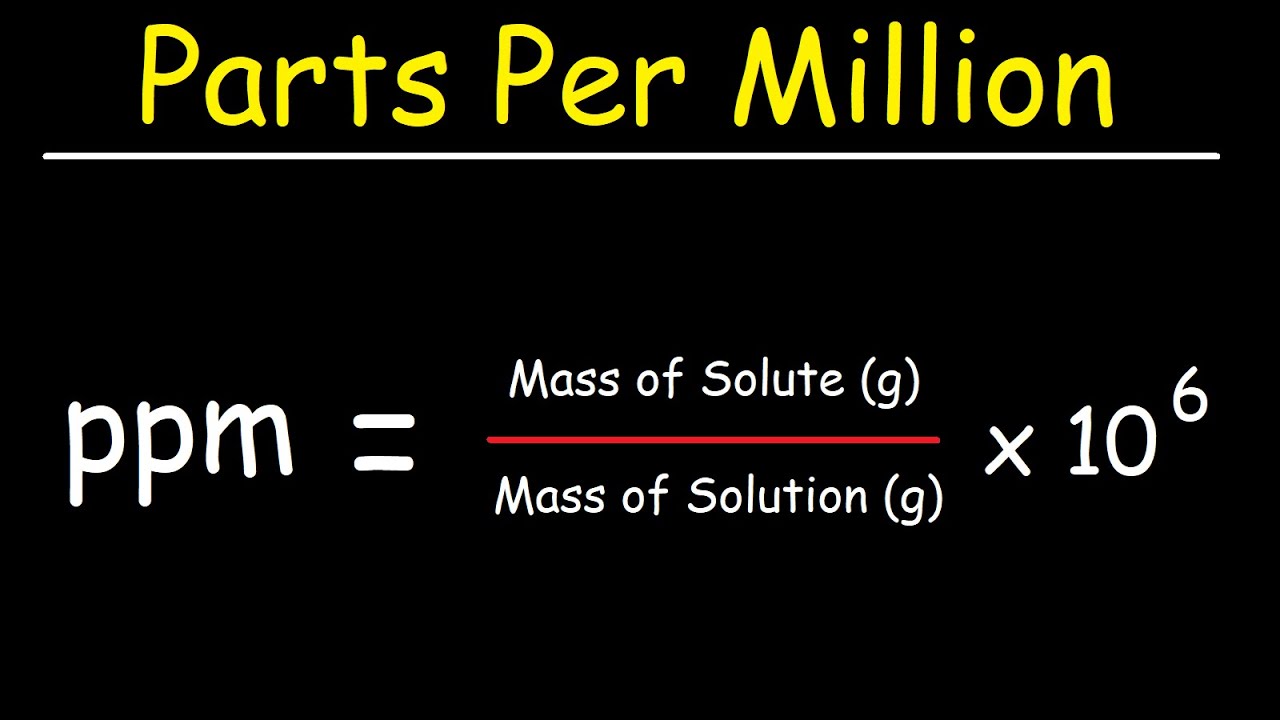What is PPM? This question is crucial in various fields, including science, environmental studies, and engineering. Parts Per Million (PPM) is a unit of measurement that expresses the concentration of one substance in a million units of another. Understanding PPM is essential for analyzing data across multiple disciplines and ensuring safety and compliance in various industries. In this article, we will delve into the definition of PPM, its applications, and its significance in different contexts. We aim to provide a comprehensive overview that caters to both beginners and experts, allowing readers to grasp the concept thoroughly.
As we navigate through the intricacies of PPM, we will explore its relevance in environmental science, chemistry, and even in everyday applications. The versatility of PPM makes it a vital metric in assessing concentrations of pollutants, chemicals, and other substances. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of what PPM is and how it impacts various sectors.
This article is structured to provide detailed insights into PPM, including its calculations, comparisons with other measurement units, and practical applications. We will also address common misconceptions and provide statistics to illustrate the importance of understanding PPM in real-world scenarios. Let’s dive into the details!
Table of Contents
- Definition of PPM
- How to Calculate PPM
- Applications of PPM
- Comparing PPM with Other Units
- Common Misconceptions about PPM
- The Importance of Understanding PPM
- Conclusion
Definition of PPM
PPM stands for Parts Per Million, a unit of measurement used to denote very dilute concentrations of substances. To put it simply, one part per million means that in one million units of a particular solution, there is one unit of the substance in question. For example, if you had a solution containing 1 milligram of a chemical in 1 liter of water, that would be expressed as 1 PPM.
PPM is widely used in various fields, particularly in environmental science to measure pollutant concentrations and in chemistry for dilutions and reactions. Its versatility allows scientists and engineers to communicate concentrations clearly and effectively.
How to Calculate PPM
Calculating PPM is straightforward. The basic formula for calculating PPM is:
- PPM = (mass of solute / mass of solution) x 1,000,000
For example, if you have 2 grams of salt dissolved in 1,000,000 grams of water, the calculation would be:
- PPM = (2 g / 1,000,000 g) x 1,000,000 = 2 PPM
This formula can apply to various contexts, whether you are measuring chemicals in water, air pollutants, or even ingredients in food.
Applications of PPM
PPM is utilized in several fields, each with specific applications and significance. Below are some of the most notable applications of PPM:
PPM in Environmental Science
In environmental science, PPM is crucial for assessing the concentration of pollutants in air, water, and soil. Regulatory bodies often set permissible limits for various pollutants, expressed in PPM, to ensure safety and environmental sustainability. For example:
- Air quality measurements often report concentrations of pollutants like carbon monoxide and sulfur dioxide in PPM.
- Water quality testing measures contaminants such as lead and arsenic in PPM to protect public health.
PPM in Chemistry
In chemistry, PPM is used to express the concentration of a solute in a solution. This is particularly important in reactions where precise measurements are critical. For laboratory experiments, understanding the PPM of reactants can affect the outcome significantly. For instance:
- Analytical chemistry often uses PPM to quantify concentrations of substances in samples.
- Pharmaceuticals require accurate PPM measurements to ensure safe and effective dosages.
PPM in Industrial Applications
Industries also rely on PPM to monitor and control the quality of products. For example:
- Manufacturing processes may specify tolerances in PPM for contaminants in raw materials.
- Food production often includes PPM measurements for additives and preservatives to ensure compliance with health regulations.
Comparing PPM with Other Units
While PPM is a widely used metric, it is essential to understand how it compares to other units of measurement, such as Percent (%), Parts Per Billion (PPB), and Parts Per Trillion (PPT).
Here are some key comparisons:
- 1 PPM = 0.001% (one part per million is one-thousandth of a percent).
- 1 PPM = 1,000 PPB (one part per million is one thousand parts per billion).
- 1 PPM = 1,000,000 PPT (one part per million is one million parts per trillion).
Understanding these conversions is crucial for professionals who deal with various concentration levels in their work.
Common Misconceptions about PPM
Despite its widespread use, several misconceptions about PPM can lead to confusion:
- PPM is often assumed to apply only to liquids, but it is applicable in gases and solids as well.
- Some people believe that a higher PPM always indicates danger, but context is crucial. For example, a high PPM may be acceptable in some industrial applications but hazardous in environmental contexts.
It is essential to understand these nuances to avoid misinterpretations and ensure accurate assessments.
The Importance of Understanding PPM
Understanding PPM is vital for several reasons:
- It helps in ensuring compliance with health and safety regulations.
- Accurate PPM measurements can improve product quality and safety.
- It aids in environmental protection by monitoring pollutant levels.
Incorporating PPM into various processes can lead to better decision-making and risk management.
Conclusion
In summary, PPM is a crucial unit of measurement that plays a significant role across various fields, from environmental science to chemistry and industrial applications. Understanding PPM helps professionals assess concentrations accurately and make informed decisions based on data. Whether you are a student, a scientist, or a worker in an industrial setting, grasping the significance of PPM is essential for effective communication and safety.
We encourage you to leave a comment below, share this article with others, or explore more articles on our website to expand your knowledge. Understanding measurement units like PPM can help contribute to better practices in your field!
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back on our site soon!